Seq2Seq
Seq2Seq是自然语言处理里非常经典的模型,以及后来引入Attention机制,在各种NLP任务中都有很好的效果。
结合Tensorflow里的源码,来一起了解下其背后的实现逻辑。
basic_rnn_seq2seq
def basic_rnn_seq2seq(encoder_inputs,
decoder_inputs,
cell,
dtype=dtypes.float32,
scope=None):
"""Basic RNN sequence-to-sequence model.
This model first runs an RNN to encode encoder_inputs into a state vector,
then runs decoder, initialized with the last encoder state, on decoder_inputs.
Encoder and decoder use the same RNN cell type, but don't share parameters.
Args:
encoder_inputs: A list of 2D Tensors [batch_size x input_size].
decoder_inputs: A list of 2D Tensors [batch_size x input_size].
cell: tf.nn.rnn_cell.RNNCell defining the cell function and size.
dtype: The dtype of the initial state of the RNN cell (default: tf.float32).
scope: VariableScope for the created subgraph; default: "basic_rnn_seq2seq".
Returns:
A tuple of the form (outputs, state), where:
outputs: A list of the same length as decoder_inputs of 2D Tensors with
shape [batch_size x output_size] containing the generated outputs.
state: The state of each decoder cell in the final time-step.
It is a 2D Tensor of shape [batch_size x cell.state_size].
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "basic_rnn_seq2seq"):
enc_cell = copy.deepcopy(cell)
_, enc_state = rnn.static_rnn(enc_cell, encoder_inputs, dtype=dtype)
return rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs, enc_state, cell)
在基本的Seq2Seq中,encode过程就是RNN输出enc_state,再进入decode RNN中。下面再看看decode的过程
def rnn_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
cell,
loop_function=None,
scope=None):
"""RNN decoder for the sequence-to-sequence model.
Args:
decoder_inputs: A list of 2D Tensors [batch_size x input_size].
initial_state: 2D Tensor with shape [batch_size x cell.state_size].
cell: rnn_cell.RNNCell defining the cell function and size.
loop_function: If not None, this function will be applied to the i-th output
in order to generate the i+1-st input, and decoder_inputs will be ignored,
except for the first element ("GO" symbol). This can be used for decoding,
but also for training to emulate http://arxiv.org/abs/1506.03099.
Signature -- loop_function(prev, i) = next
* prev is a 2D Tensor of shape [batch_size x output_size],
* i is an integer, the step number (when advanced control is needed),
* next is a 2D Tensor of shape [batch_size x input_size].
scope: VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn_decoder".
Returns:
A tuple of the form (outputs, state), where:
outputs: A list of the same length as decoder_inputs of 2D Tensors with
shape [batch_size x output_size] containing generated outputs.
state: The state of each cell at the final time-step.
It is a 2D Tensor of shape [batch_size x cell.state_size].
(Note that in some cases, like basic RNN cell or GRU cell, outputs and
states can be the same. They are different for LSTM cells though.)
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(scope or "rnn_decoder"):
state = initial_state
outputs = []
prev = None
for i, inp in enumerate(decoder_inputs):
if loop_function is not None and prev is not None:
with variable_scope.variable_scope("loop_function", reuse=True):
inp = loop_function(prev, i)
if i > 0:
variable_scope.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
output, state = cell(inp, state)
outputs.append(output)
if loop_function is not None:
prev = output
return outputs, state
decoder_inputs 其实只在训练阶段会用到。下面结合inp loop_function 一起来看看。
initial_state 也就是前面encode RNN 输出的 enc_state
RNN的输入分为当前的input 以及上一次时序的 state,也就是下面这行代码。
output, state = cell(inp, state)
训练时和测试时的区别在于inp的不同
train 阶段: inp来自 decoder_inputs
predict 阶段: inp = loop_function(prev, i)
以翻译任务为例,在训练阶段有 decode_inputs 来“指导”网络来学习。而在测试时,只能依靠前一时序的cell的输出作为上下文。
embedding_attention_seq2seq
引入Attention机制的Seq2Seq就显得复杂多了。先来看一张图,
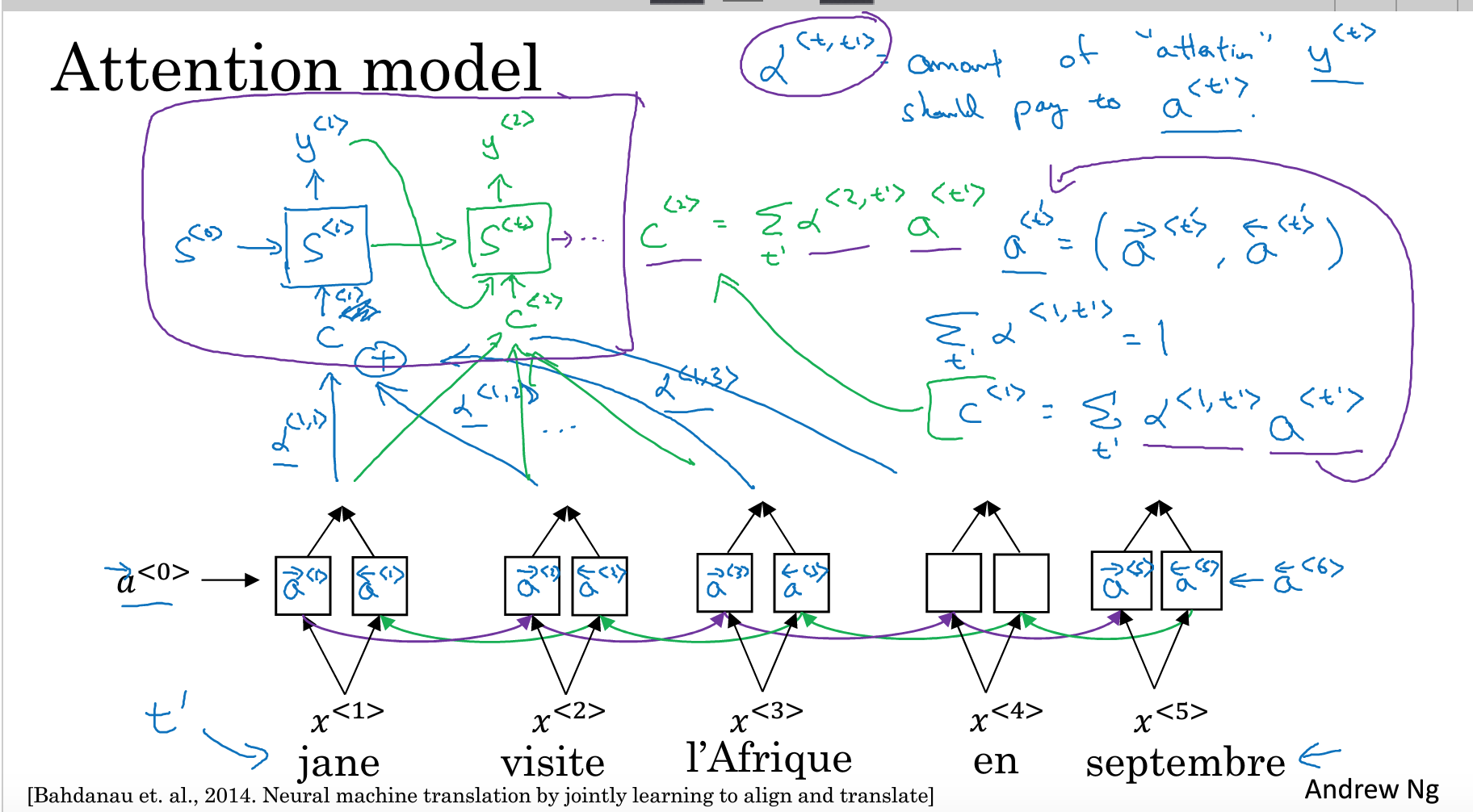
在encode过程中一系列的输出,作为decode的输入。以翻译任务为例,译文的某个单词,只与原文的某几个词相关,而不是整个句子,例如译文的第一个单词,可以由原文的前几个词的信息就能得到。也就是译文的每个单词的信息来自于原文的部分词语,也就是原文的每个词受到的”注意力”(权重)是不一样的。
def embedding_attention_seq2seq(encoder_inputs,
decoder_inputs,
cell,
num_encoder_symbols,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
num_heads=1,
output_projection=None,
feed_previous=False,
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):
"""Embedding sequence-to-sequence model with attention.
This model first embeds encoder_inputs by a newly created embedding (of shape
[num_encoder_symbols x input_size]). Then it runs an RNN to encode
embedded encoder_inputs into a state vector. It keeps the outputs of this
RNN at every step to use for attention later. Next, it embeds decoder_inputs
by another newly created embedding (of shape [num_decoder_symbols x
input_size]). Then it runs attention decoder, initialized with the last
encoder state, on embedded decoder_inputs and attending to encoder outputs.
Warning: when output_projection is None, the size of the attention vectors
and variables will be made proportional to num_decoder_symbols, can be large.
Args:
encoder_inputs: A list of 1D int32 Tensors of shape [batch_size].
decoder_inputs: A list of 1D int32 Tensors of shape [batch_size].
cell: tf.nn.rnn_cell.RNNCell defining the cell function and size.
num_encoder_symbols: Integer; number of symbols on the encoder side.
num_decoder_symbols: Integer; number of symbols on the decoder side.
embedding_size: Integer, the length of the embedding vector for each symbol.
num_heads: Number of attention heads that read from attention_states.
output_projection: None or a pair (W, B) of output projection weights and
biases; W has shape [output_size x num_decoder_symbols] and B has
shape [num_decoder_symbols]; if provided and feed_previous=True, each
fed previous output will first be multiplied by W and added B.
feed_previous: Boolean or scalar Boolean Tensor; if True, only the first
of decoder_inputs will be used (the "GO" symbol), and all other decoder
inputs will be taken from previous outputs (as in embedding_rnn_decoder).
If False, decoder_inputs are used as given (the standard decoder case).
dtype: The dtype of the initial RNN state (default: tf.float32).
scope: VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to
"embedding_attention_seq2seq".
initial_state_attention: If False (default), initial attentions are zero.
If True, initialize the attentions from the initial state and attention
states.
Returns:
A tuple of the form (outputs, state), where:
outputs: A list of the same length as decoder_inputs of 2D Tensors with
shape [batch_size x num_decoder_symbols] containing the generated
outputs.
state: The state of each decoder cell at the final time-step.
It is a 2D Tensor of shape [batch_size x cell.state_size].
"""
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
scope or "embedding_attention_seq2seq", dtype=dtype) as scope:
dtype = scope.dtype
# Encoder.
encoder_cell = copy.deepcopy(cell)
encoder_cell = core_rnn_cell.EmbeddingWrapper(
encoder_cell,
embedding_classes=num_encoder_symbols,
embedding_size=embedding_size)
encoder_outputs, encoder_state = rnn.static_rnn(
encoder_cell, encoder_inputs, dtype=dtype)
# First calculate a concatenation of encoder outputs to put attention on.
top_states = [
array_ops.reshape(e, [-1, 1, cell.output_size]) for e in encoder_outputs
]
attention_states = array_ops.concat(top_states, 1)
# Decoder.
output_size = None
if output_projection is None:
cell = core_rnn_cell.OutputProjectionWrapper(cell, num_decoder_symbols)
output_size = num_decoder_symbols
if isinstance(feed_previous, bool):
return embedding_attention_decoder(
decoder_inputs,
encoder_state,
attention_states,
cell,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
num_heads=num_heads,
output_size=output_size,
output_projection=output_projection,
feed_previous=feed_previous,
initial_state_attention=initial_state_attention)
# If feed_previous is a Tensor, we construct 2 graphs and use cond.
def decoder(feed_previous_bool):
reuse = None if feed_previous_bool else True
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=reuse):
outputs, state = embedding_attention_decoder(
decoder_inputs,
encoder_state,
attention_states,
cell,
num_decoder_symbols,
embedding_size,
num_heads=num_heads,
output_size=output_size,
output_projection=output_projection,
feed_previous=feed_previous_bool,
update_embedding_for_previous=False,
initial_state_attention=initial_state_attention)
state_list = [state]
if nest.is_sequence(state):
state_list = nest.flatten(state)
return outputs + state_list
outputs_and_state = control_flow_ops.cond(feed_previous,
lambda: decoder(True),
lambda: decoder(False))
outputs_len = len(decoder_inputs) # Outputs length same as decoder inputs.
state_list = outputs_and_state[outputs_len:]
state = state_list[0]
if nest.is_sequence(encoder_state):
state = nest.pack_sequence_as(
structure=encoder_state, flat_sequence=state_list)
return outputs_and_state[:outputs_len], state
encoder阶段,基本和之前类似
...
encoder_outputs, encoder_state = rnn.static_rnn(
encoder_cell, encoder_inputs, dtype=dtype)
...
decoder阶段,重点看attention_decoder
def attention_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
attention_states,
cell,
output_size=None,
num_heads=1,
loop_function=None,
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):
...
initial_state:也就是之前encode输出的encoder_state
attention_states:之前encode输出的encoder_outputs,也就是RNN的中间输出结果。
结合论文里的公式,尝试理解下代码。
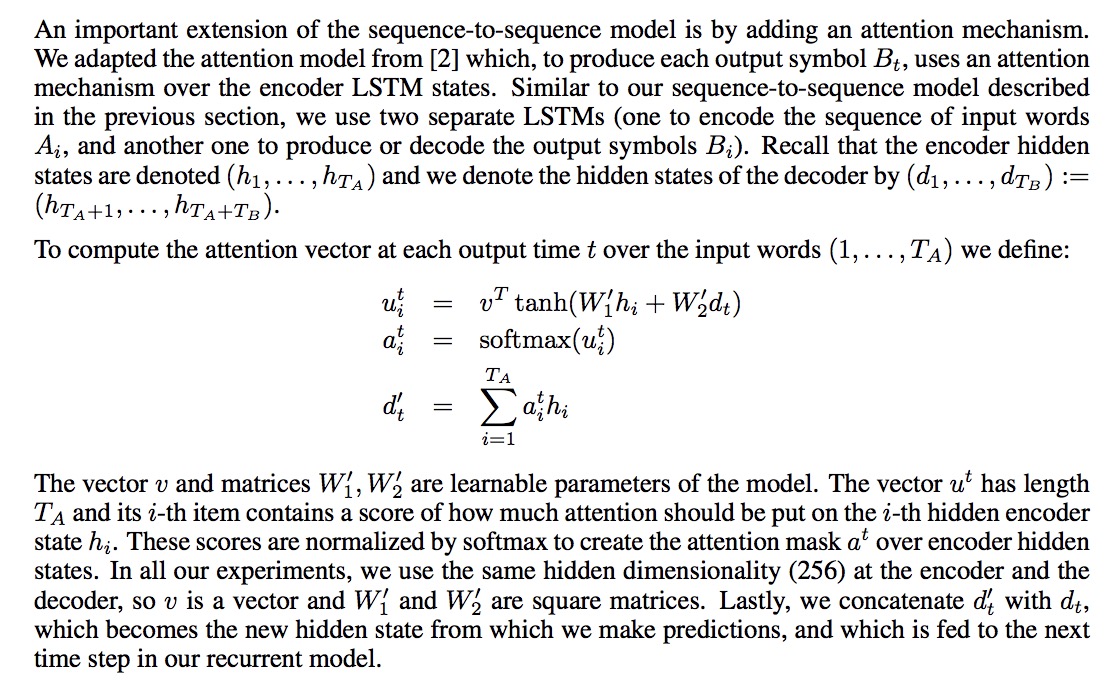
hidden = array_ops.reshape(attention_states,
[-1, attn_length, 1, attn_size])
hidden_features = []
v = []
attention_vec_size = attn_size # Size of query vectors for attention.
for a in xrange(num_heads):
k = variable_scope.get_variable(
"AttnW_%d" % a, [1, 1, attn_size, attention_vec_size],
dtype=dtype)
hidden_features.append(nn_ops.conv2d(hidden, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], "SAME"))
v.append(
variable_scope.get_variable(
"AttnV_%d" % a, [attention_vec_size], dtype=dtype))
这里是计算W1 * ht。这里参数num_heads表示多组weight set,默认是1。计算attention的时候,可以用多组weight。
v:对应公式里的v,也是要学习的参数
def attention(query):
"""Put attention masks on hidden using hidden_features and query."""
ds = [] # Results of attention reads will be stored here.
if nest.is_sequence(query): # If the query is a tuple, flatten it.
query_list = nest.flatten(query)
for q in query_list: # Check that ndims == 2 if specified.
ndims = q.get_shape().ndims
if ndims:
assert ndims == 2
query = array_ops.concat(query_list, 1)
for a in xrange(num_heads):
with variable_scope.variable_scope("Attention_%d" % a):
y = Linear(query, attention_vec_size, True)(query)
y = array_ops.reshape(y, [-1, 1, 1, attention_vec_size])
y = math_ops.cast(y, dtype)
# Attention mask is a softmax of v^T * tanh(...).
s = math_ops.reduce_sum(v[a] * math_ops.tanh(hidden_features[a] + y),
[2, 3])
a = nn_ops.softmax(math_ops.cast(s, dtype=dtypes.float32))
# Now calculate the attention-weighted vector d.
a = math_ops.cast(a, dtype)
d = math_ops.reduce_sum(
array_ops.reshape(a, [-1, attn_length, 1, 1]) * hidden, [1, 2])
ds.append(array_ops.reshape(d, [-1, attn_size]))
return ds
这里就是计算attention的阶段,query也就是前一时序RNN输出的state。
d=a*hidden
hidden也就是encode过程输出的encoder_state
d = math_ops.reduce_sum(
array_ops.reshape(a, [-1, attn_length, 1, 1]) * hidden, [1, 2])
得到attention部分,再加上decode_input
...
inputs = [inp] + attns
inputs = [math_ops.cast(e, dtype) for e in inputs]
x = Linear(inputs, input_size, True)(inputs)
# Run the RNN.
cell_output, state = cell(x, state)
# Run the attention mechanism.
if i == 0 and initial_state_attention:
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True):
attns = attention(state)
else:
attns = attention(state)
参考
2、https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.7449.pdf
3、https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.0473.pdf
5、https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27769667